Alarming Predicament for Honey Bees: Understanding the current challenges facing our furry pollinators
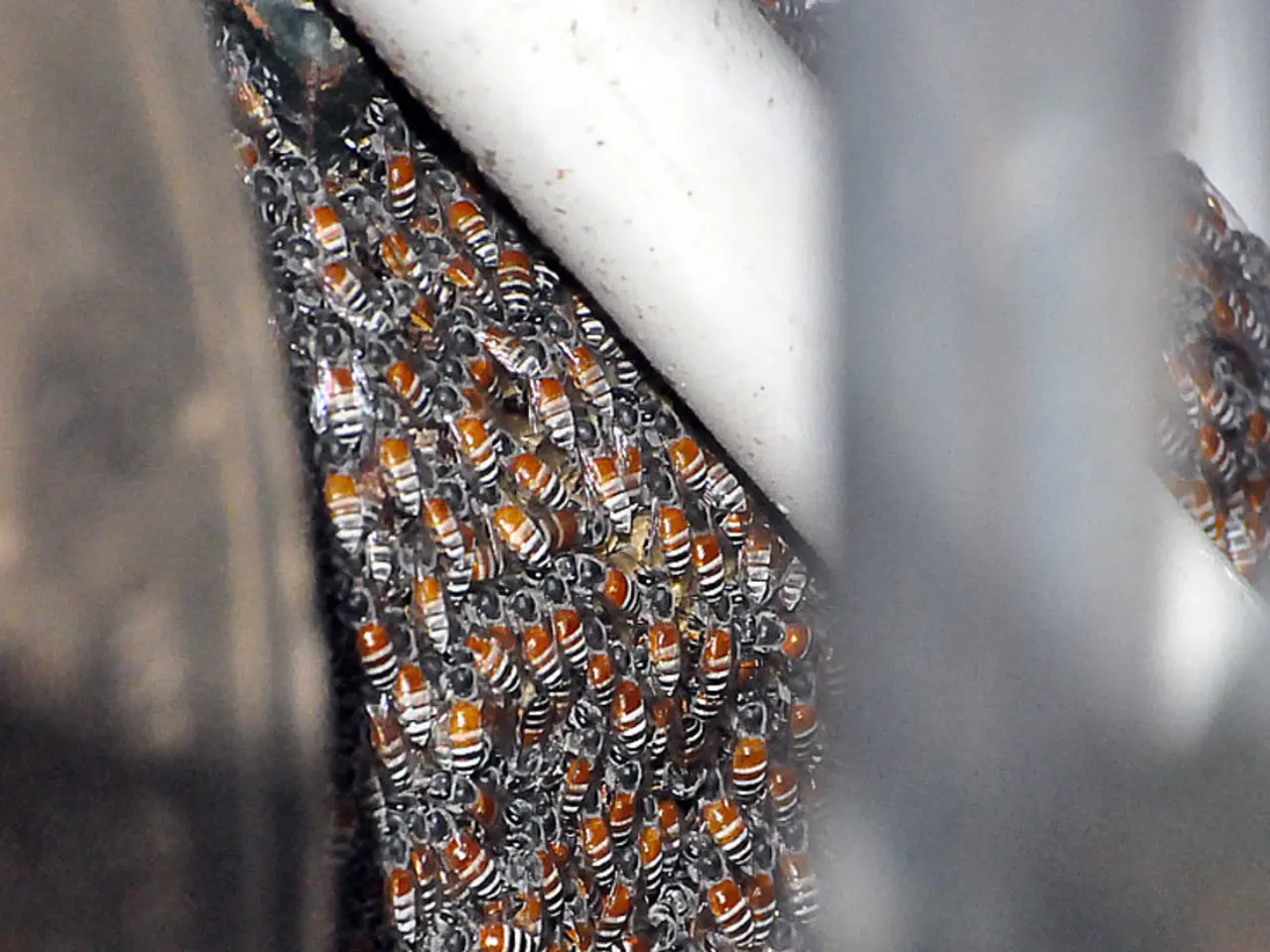
In the heart of our bustling world, the humble honey bee is facing a significant crisis. Climate change, habitat loss, diseases, and pesticide exposure are causing problems for these essential pollinators, impacting the production of various agricultural products worth billions.
Honey bees are instrumental in food security, pollinating crops such as avocados, blueberries, peaches, pumpkins, sunflowers, almonds, cucumbers, and more. Their drastic decline threatens food production, biodiversity, and the broader ecosystem.
The consequences of this decline are far-reaching for humans. Reduced crop yields and food diversity lead to higher food prices and decreased availability of nutritious foods. The U.S. commercial beekeeping industry lost over 60% of its colonies between 2024 and 2025, translating to around $600 million in lost revenue.
The ecological chain could also suffer as plants dependent on bee pollination decline, impacting herbivores and carnivores, potentially triggering species and habitat losses. Agricultural income decline, rural unemployment, potential food crises, and social unrest may result from reduced pollination and food shortages.
Key factors contributing to the decline include Varroa destructor mites resistant to pesticides, habitat loss, climate change, pesticide exposure, and diseases. The continued decline of commercial honey bees, which pollinate over 100 crops in the U.S. alone, poses a substantial risk to global food security and agricultural economies.
However, there are ways to help support the honey bee population. Planting pollen-rich plants, creating bee baths or water feeders, and donating to organisations like The Bee Conservancy, can all make a difference. The Bee Conservancy, based in New York City, focuses on protecting the bee population and educating the public on their importance.
The honey bee population in the United States is in an overall decline, with the number of colonies decreasing from 2.89 million in October 2022 to 2.71 million in April 2023. Scientists are breeding honey bees to create ones that can identify and bite the legs of varroa mites, making them incapable of attaching to the bees.
Despite their small size, the average honey bee is around 0.5 inches long, while the queen bee is around 0.8 inches long. Domesticated honey bees make their homes in bee boxes and have their honey collected by beekeepers without harming the bees.
The decline in the honey bee population is not a future prediction but a reality that we are facing now. As Shahi Mahonaj '24, the Gardening Club Co-President at Bronx Science, states, "honey bees play an important role in supporting our population and should be supported in return." Let's do our part to help these vital insects and secure our food supply for the future.
Read also:
- Reinventing Parental Roles Through Self-Healing: A Prominent Approach Drawing from Therapy Practices
- Forging Ahead: Collaborating Towards an Eco-friendly Tomorrow
- AI Training's Hidden Exploitation: Outlier, DataAnnotation.tech, and the Gig Platforms Amplifying the AI Revolution
- Escaping a False Religion: Comprehensive Guide for Liberation