The role of law in fostering red tape and bureaucracy?
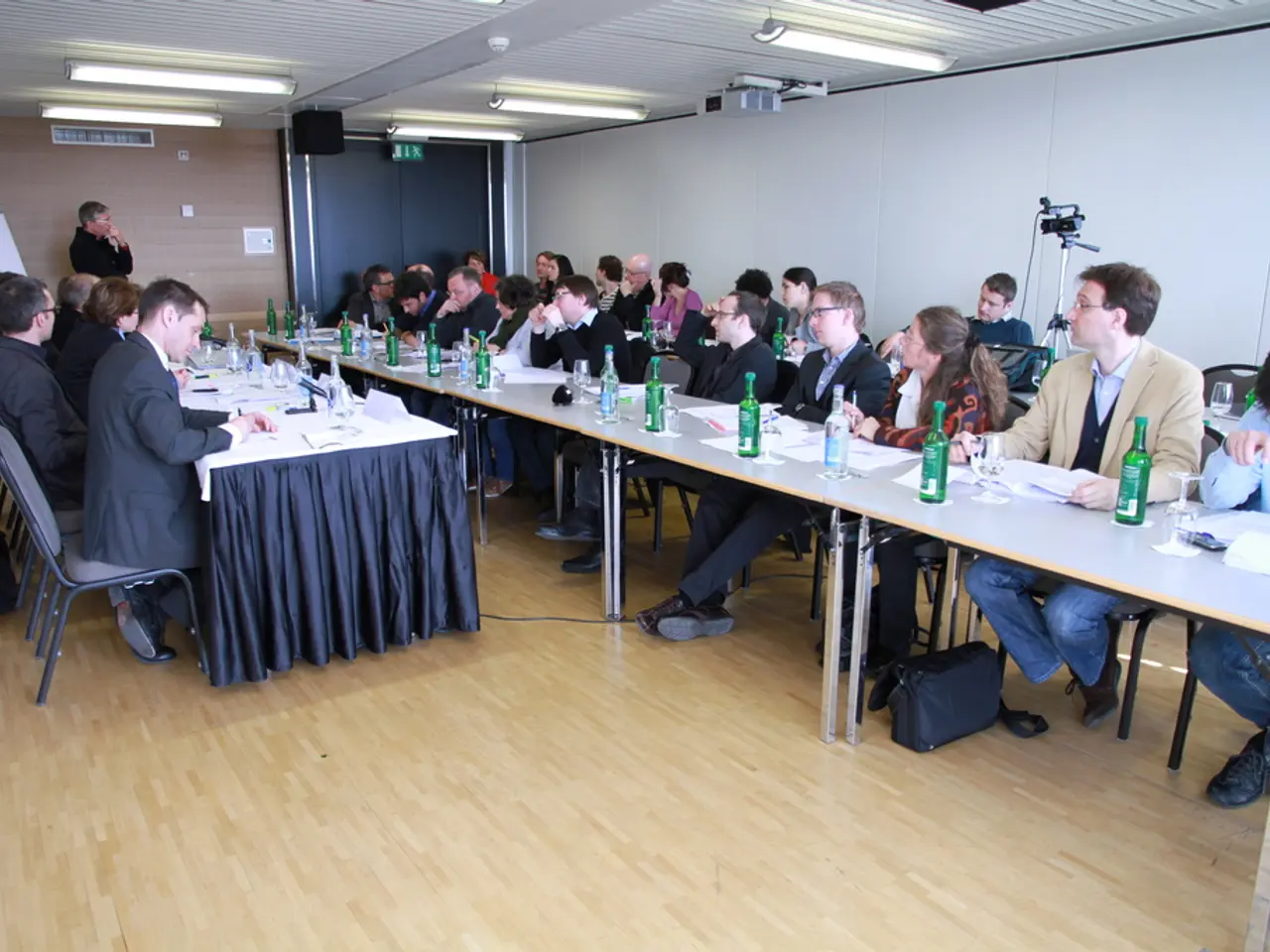
In a series of discussions at the Hochschule für Verwaltung und Finanzen Ludwigsburg (HVF), experts and policymakers have been exploring ways to reduce bureaucratic burdens while maintaining the rule of law.
Andrea Versteyl, a specialist lawyer for administrative law, emphasized that legal application always generates effort. She suggested that administrative burden reduction must start with the laws themselves. Versteyl argued that result-oriented administrative action is needed, and the density and depth of regulations are currently exaggerated.
Iris Rauskala, rector of the HVF, questioned whether there is too much bureaucracy or just too much bad regulation. Patrick Wegener, head of the European Office of the European municipalities and a graduate of HVF, has high hopes for the Omnibus procedure established by EU Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, which provides simplifications for companies but not yet for municipalities.
Jörg Krauss, State Minister, summarized that much of what we perceive as bureaucracy is a reaction to societal change. He highlighted that authorities should see themselves as part of the solution, especially when considering the concerns of businesses. Krauss held public service accountable for common practices like rejecting applications if a point is missing.
The first event in the planned series focused on a status quo analysis and tracing the roots, with scientists and experts from practice dealing with specific aspects of administration and law. The conference aimed to contribute to systematically examining the topic of bureaucracy and de-bureaucratization.
In the context of healthcare, reforms like establishing centralized clearinghouses for bill submission, simplifying prior authorization, enforcing interoperable data standards, and integrating telehealth and automation technologies can significantly reduce administrative burden while maintaining compliance with legal regulations.
Similarly, governmental executive orders aim to reduce bureaucracy by eliminating non-statutory functions and minimizing statutory roles of some agencies, ensuring all actions remain grounded in existing laws so that rule of law is preserved.
However, EU regulations for AI deployment result in duplicative information obligations, IT security requirements, and notification obligations to supervisory authorities. Julius Mihm, mayor of Schwäbisch Gmünd, criticized the European level for causing problems, such as the tendering of a kindergarten unit for 25 children throughout Europe, which incurs additional costs of around 60,000 euros and delays planning by half a year.
Many mayors are now wanting to break the chains of bureaucracy. According to Professor Judith Klink-Straub of the HVF Institute for IT and Data Protection Law, the EU went too far with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) a few years ago, resulting in a reversal of the burden of proof without legal regulation.
In essence, reducing bureaucratic burdens requires simplifying procedures, centralizing tasks, automating record-keeping, coordinating regulations, and integrating digital solutions while respecting legal mandates to maintain rule of law integrity. Laws set frameworks that require bureaucratic structures for implementation and compliance, making law a direct driver of bureaucratic expansion. Efficient rule of law administration balances legal requirements with pragmatic administrative design to avoid unnecessary bureaucracy.
- To address the issue of excessive bureaucracy, Andrea Versteyl suggests starting with a reevaluation of laws and regulations, advocating for result-oriented administrative action to reduce density and depth.
- In the realm of politics and policy-making, governmental executive orders aim to reduce bureaucracy by eliminating non-essential functions, ensuring all actions align with existing laws to preserve the rule of law.